Modern technology continues to advance at astonishing speeds, and recent years have given us plenty of remarkable developments in the fintech sector in particular. Improvements were long overdue, and thanks to rapid modernisation within the industry, customers are now enjoying a far better experience. However, we’re only at the beginning of the cross-border payment revolution. As the change becomes reality, it’s the financial institutions that will be expected to step up and provide efficient cross-border payment systems that their clients demand — especially in regions where the need for trusted, reliable cross-border payments is increasing rapidly. With goods and services moving more quickly and across greater distances than ever before,customers are increasingly demanding cross-border payments that are as seamless and convenient as domestic ones.
What Are Cross-Border Payments?
- Today’s e-commerce world has a global reach. Payments, remittances, and purchases all often require money exchanged across borders.Cross-border payments are transactions where the payee and the transaction recipient are based in separate countries.The transactions can be between individuals, companies or banking institutions who are looking to transfer funds across territories. For merchants who are operating internationally, it is crucial that they are able to accept payments across all countries that they are targeting. Many different scenarios need to be accounted for when a merchant needs to deal with international payments because each country has its own set of rules. The demand for cross-border payments is so high that steps are being made to improve cross-border payments as a whole.
- Over the past few decades, the increased international mobility of goods and services, capital and people has contributed to the growing economic importance of cross-border payments. Factors that have supported the growth in cross-border payments include manufacturers expanding their supply chains across borders, global investment flows and international trade and e-commerce.
Insights
- India is the largest Global Market at around $ 83 Billion , for Inward Remittance flow followed by China and Mexico according to a PWC report released in July.
- Cross Border Payments undergo multiple level of verifications in each country. International payments require foreign transaction fees , and dealing in exchange rates. When a transaction is executed various local entities have to work together to transfer the funds.
- India and Singapore are working to link their digital payments systems to enable “instant, low-cost fund transfers,” in a major push to disrupt the cross-border transactions between the two nations that amounts to over $1 billion each year.
- The project to link India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI) and Singapore’s PayNow is targeted for operationalization by July 2022. Users on either of the systems will be able to make transactions to one another without having to sign up to the second platform, the banks added.
- “When implemented, fund transfers can be made from India to Singapore using mobile phone numbers, and from Singapore to India using UPI virtual payment addresses (VPA). The experience of making a PayNow transfer to a UPI VPA will be similar to that of a domestic transfer to a PayNow VPA,” said Monetary Authority of Singapore in a press statement.
- India’s central bank described the project as a “significant milestone in the development of infrastructure for cross-border payments” between India and Singapore, and said the linkage “closely aligns with the G20’s financial inclusion priorities of driving faster, cheaper and more transparent cross-border payments.”
Cross-Border Payments Landscape
Despite the availability of conventional modes, transaction fees and excessive regulatory and documentation requirements make small-value transactions unattractive. The cost and speed of delivery strongly influence the customer’s final selection of payment mode. Recently, FinTechs have leveraged technology and captured the white space in cross-border payments left unaddressed by legacy models.Since 2016, India’s cross-border remittances have been growing steadily at a CAGR of 8%,driven by the increase in global mobility of goods and services, international travel and international workforce.
Past
- Correspondent Bank/Swift: Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunications (SWIFT) system is a vast messaging network used by banks and other financial institutions to quickly, accurately, and securely send and receive information, such as money transfer instructions. Indian banks tie up with foreign correspondent banks and open a NOSTRO account. The correspondent and Indian bank process the transfer request through the SWIFT messaging infrastructure.
- Money Transfer Saving Scheme: MTSS is a strategic tie-up between overseas principals and Indian agents who disburse funds to beneficiaries in India at ongoing exchange rates.
- Rupee Drawing Arrangement: Rupee Drawing Arrangement (RDA) is a channel to receive cross-border remittances from overseas jurisdictions. Under this arrangement, the Authorised Category I banks enter into tie-ups with the non-resident Exchange Houses in the FATF compliant countries to open and maintain their Vostro Account.
- Postal Channels: The International Financial System (IFS) is a software/platform developed by the Universal Postal Union (UPU) to facilitate both inward and outward remittances through the postal channel across partner countries. These transfers are conducted over electronic data interchange (EDI) messages from India Post’s central server to the IFS national server to the destination country postal operator through the UPU system.
New Current
Emergence Of Fintech: FinTechs have leveraged technology to introduce low-cost solutions for international payments for individuals, small businesses and corporates. FinTechs have revolutionised the cross-border payments ecosystem through enhanced customer service, extensive global reach, flexible payment options, lower fees, and reduced transaction times.FinTech companies facilitate transfers in a secure, fast and affordable way.Each cross-border transaction consists of a set of two individual domestic transactions. Settlement between accounts/offices is done several times a month to optimise exchange rates. The transfer fees range from 0.25–3% of the transaction amount and depend on the destination.
Future Models
- Faster Payment Rails: FinTechs are leveraging entrenched faster payment rails to offer seamless cross-border payment services. The transactions will be funded through the user’s bank account or registered card. Integration of UPI with the faster payment systems of Singapore and Thailand, which uses proxy identifiers like mobile numbers, will enable payments through this route. This would reduce the information and effort required for cross-border payments. The partnership will help FinTech companies to expand their presence in several markets and more aggressively compete with rivals that have a wider reach.
- Distributed Ledger Technology (Dlt): FinTechs, banks and IT companies have been experimenting with DLT in the cross-border remittance space. This model uses a bidirectional messaging and settlement component that validates transactions using DLT before funds are transferred.This model is gaining increasing acceptance among customers who transfer smaller amounts of money, particularly in small-to-medium businesses.
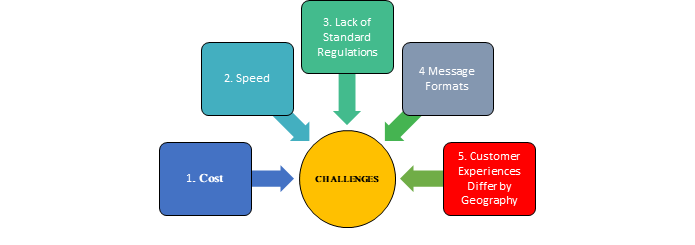
Key Challenges: Cross-border payments involve different time zones and different currencies. Multiple compliance checks add layers of friction such as significant delays, exorbitant charges and uncertain receipt of payment. Innovation and partnership among stakeholders can help in addressing challenges around speed, cost and transparency in cross-border payments
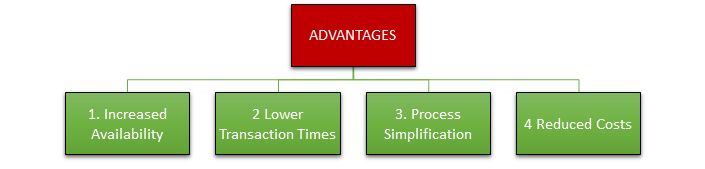
Advantages:
Cross Border Payments has few Advantages also which are listed below :
Final Thoughts
For merchants looking to expand their markets overseas, it is integral that they are knowledgeable about cross-border payments. Keeping up to date with the latest innovations will provide your customers with the best payment experience possible and encourage return custom. The mechanisms of international payments can be complicated, so it is worth partnering with an experienced PSP who will help you overcome any challenges. As the economy becomes more interconnected across borders, there is a growing appetite for fast, efficient and accessible payments to be made in every part of the world.
With growth in eCommerce, global trade and migration, cross-border payments are on the rise for both businesses and consumers, from family members sending money to their native countries to growth in online marketplaces. Many initiatives are underway with central banks, international organizations and the private sector – all of which are innovating to address persistent barriers and gaps. However Compliance with anti-money laundering and anti-terrorism financing regulation will be the most persistent challenges in cross-border payments.